Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Moribayashi, Kengo
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 365(Part B), p.592 - 595, 2015/12
Hiroki, Akihiro; Yamashita, Shinichi*; Kimura, Atsushi; Nagasawa, Naotsugu; Taguchi, Mitsumasa
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 365(Part B), p.583 - 586, 2015/12
Effects of liner energy transfer (LET) and dose rate on the optical property of polymer gel dosimeters were investigated. The dosimeter prepared by using a radiation-crosslinked hydroxypropyl cellulose gel and methacrylate monomers such as 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate and nonaethylene glycol dimethacrylate showed the color change from colorless to white with the He, C, Fe ions irradiation. Absorbance of the irradiated dosimeters increased with the dose up to 10 Gy. The absorbance of the dosimeters at the same total dose decreased with increasing dose rate in the range of 0.1 to 6.8 Gy/min. The absorbance decreased in order of He, C, Fe ions, which was in agreement with a change of LET. The increase in LET affected the decrease in the number of polymerization initiator such as OH radical and hydrated electron, resulting in the reduction of the absorbance of the dosimeters.
 crystals
crystalsYanagida, Takayuki*; Koshimizu, Masanori*; Kurashima, Satoshi; Iwamatsu, Kazuhiro*; Kimura, Atsushi; Taguchi, Mitsumasa; Fujimoto, Yutaka*; Asai, Keisuke*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research B, 365(Part B), p.529 - 532, 2015/12
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:67.09(Instruments & Instrumentation)We measured temporal profiles of scintillation of Ce-doped LiCaAlF scintillator crystals at different linear energy transfers (LETs). Based on the comparison of the high-LET temporal profiles with those at low LET, we found that a fast component was observed only at low LET. The disappearance of the fast component at high LET is tentatively ascribed to quenching of excited states at defects owing to the interaction between excited states via Auger process. In addition, the rise and the initial decay behavior was dependent on the LET. This LET-dependent behavior is explained by a seeming acceleration process and a slowing down process in energy transfer at high LET. The LET-dependent temporal profiles provide a basis of discrimination technique of
scintillator crystals at different linear energy transfers (LETs). Based on the comparison of the high-LET temporal profiles with those at low LET, we found that a fast component was observed only at low LET. The disappearance of the fast component at high LET is tentatively ascribed to quenching of excited states at defects owing to the interaction between excited states via Auger process. In addition, the rise and the initial decay behavior was dependent on the LET. This LET-dependent behavior is explained by a seeming acceleration process and a slowing down process in energy transfer at high LET. The LET-dependent temporal profiles provide a basis of discrimination technique of  -ray and neutron detection events using these scintillators based on the nuclear reaction,
-ray and neutron detection events using these scintillators based on the nuclear reaction,  Li(n,
Li(n, )t.
)t.
Ishikawa, Norito; Okubo, Nariaki; Taguchi, Tomitsugu
no journal, ,
In this study, CeO and NiO were irradiated with Au ions in the energy range of 200-340 MeV at oblique incidence. Observation of as-irradiated samples by transmission electron microscope (TEM) shows that hillocks are created not only at the wide faces but also at the crack faces of thin samples. Since the hillocks created at the crack faces can be imaged by TEM, their shape and crystallographic features can be revealed by TEM. From the images of hillocks created at the crack faces, many of the hillocks are found to be spherical for ion-irradiated CeO
and NiO were irradiated with Au ions in the energy range of 200-340 MeV at oblique incidence. Observation of as-irradiated samples by transmission electron microscope (TEM) shows that hillocks are created not only at the wide faces but also at the crack faces of thin samples. Since the hillocks created at the crack faces can be imaged by TEM, their shape and crystallographic features can be revealed by TEM. From the images of hillocks created at the crack faces, many of the hillocks are found to be spherical for ion-irradiated CeO . For ion-irradiated NiO, atomic-scale steps are found to be created at the top surface of the hillocks. We present an experimental evidence that hillocks created for both oxides irradiated with swift heavy ions have a crystal structure whose lattice spacing and orientation coincide with those of the matrix.
. For ion-irradiated NiO, atomic-scale steps are found to be created at the top surface of the hillocks. We present an experimental evidence that hillocks created for both oxides irradiated with swift heavy ions have a crystal structure whose lattice spacing and orientation coincide with those of the matrix.
Kitamura, Akane; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Yuri, Yosuke; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Sawada, Shinichi; Yuyama, Takahiro
no journal, ,
Nuryanthi, N.*; Yamaki, Tetsuya; Kitamura, Akane; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Yoshimura, Kimio; Sawada, Shinichi; Asano, Masaharu*; Maekawa, Yasunari; Suzuki, Akihiro*; Terai, Takayuki*
no journal, ,
We have used the ion-track grafting technique for developing an anion exchange membrane for fuel cell applications. In order to obtain the membrane, a vinyl benzyl chloride (VBC) was grafted into an ion-irradiated poly(ethylene-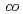 -tetrafluoroethylene) film. This study deals with investigation of the radicals remaining in each track and the VBC grafting with a variety of ion beams from the TIARA cyclotron. The accelerated ions with different masses and energies enabled us to clarify the effect of the LET and radial dose distribution in the track on the VBC grafting. Such extensive research will bring us interesting knowledge relating the track structures to the resulting membrane properties.
-tetrafluoroethylene) film. This study deals with investigation of the radicals remaining in each track and the VBC grafting with a variety of ion beams from the TIARA cyclotron. The accelerated ions with different masses and energies enabled us to clarify the effect of the LET and radial dose distribution in the track on the VBC grafting. Such extensive research will bring us interesting knowledge relating the track structures to the resulting membrane properties.
Yamaki, Tetsuya; Nuryanthi, N.*; Koshikawa, Hiroshi; Asano, Masaharu*; Sawada, Shinichi; Kitamura, Akane; Maekawa, Yasunari; Kay-Obbe, V.*; Severin, D.*; Seidl, T.*; et al.
no journal, ,
Practically, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) has been said to be the only fluoropolymer in which ion tracks can be developed by chemical etching. We thus investigated the possibility of varying the beam parameters and applying the effect of a pre-etching treatment for PVDF ion-track membranes with the goal of achieving enhanced track etching for effective control of the pore size and shape. Our activities also cover all types of fluoropolymers including PVDF. Compared to PVDF, poly(ethylene-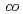 -tetrafluoroethylene) and a series of perfluoropolymers are known to be very stable in highly-concentrated acid or alkaline solutions or at higher temperatures. Although this property might make their ion-track etching very challenging, the ongoing research is expected to allow one to accumulate know-how on methods of chemical etching, which can be generalized for the chemical structures. These will give feedback to a guiding principle for effective ion-track etching in fluoropolymers.
-tetrafluoroethylene) and a series of perfluoropolymers are known to be very stable in highly-concentrated acid or alkaline solutions or at higher temperatures. Although this property might make their ion-track etching very challenging, the ongoing research is expected to allow one to accumulate know-how on methods of chemical etching, which can be generalized for the chemical structures. These will give feedback to a guiding principle for effective ion-track etching in fluoropolymers.